How effective is the ARP that check...
02
09
How effective is the ARP that checks the MAC address from the IP address?
The time for the quiz "Who is the correct answer?"In this quiz, Kenichi, Izumi -chan, and Takeda -kun answer my questions.However, only one person is correct.The theme of the quiz is "TCP/IP", the basics of network.By the way, who is the correct answer?
Who is the correct answer?(Be careful because there are two mistakes!)
Check the MAC address from the IP address in ARP
In the network built with Ethernet, the IP packet is sent and received in a data format called "Ethernet frame" (Fig. 1).The header of the Ethernet frame is mainly composed of three fields: Media Access Control Address, mainly destination and source.Ethernet cards have a unique MAC address, and Ethernet uses this MAC address information to send and receive Ethernet frames.
Figure 1 ● IP hierarchy and Ethernet frame
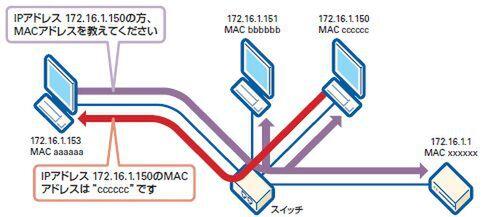
On the other hand, IP addresses are used in IP.In other words, communication with IP using Ethernet is performed using two addresses, IP address and MAC address.Therefore, in order to communicate IP with Ethernet, it is necessary to check the destination MAC address from the IP address to which the destination IP address each time.
The protocol that examines this MAC address is "ARP (Arp)".In ARP, the IP address that you want to know the MAC address is sent to all adjacent hosts (communication to all hosts).Then, receive the MAC address as a response from the host with the corresponding IP address (Fig. 2).
Figure 2 ● ARP operation in a single network
Packet transfer via router
The point here is when there are two networks as shown in Fig. 3, and the destination host is on the network across the router.Since the IP address can indicate the network (where) and the host (someone), the destination can be specified across multiple networks.In the IP network, it is possible to send an IP packet to a different network by transferring packets to the router.
Figure 3 ● ARP operation across the router
However, Ethernet frames cannot be crossed over the router and can only communicate with adjacent nodes connected by hubs or switches.In addition, there is a restriction that the communication of the IP broadcast used in the ARP request cannot be exceeded the router.In other words, as long as you send an ARP request on the Ethernet broadcast, you cannot send an ARP request beyond the router.
Therefore, check the IP address of the router (GW in the figure) (specified as a default gateway on each host), and then examine the MAC address of the router with ARP.Then, send the data frame to the router.If you explain this in Figure 3, 172.16.1.153 to 10.0.0.To send an IP packet to 100, you once send an IP packet to the router.
Here, the router removes the IP packet from the received Ethernet frame, but since the destination written on the IP header is not the router, the packet will be transferred to the destination IP address again.Again, execute the ARP for the destination IP address from the router to examine the MAC address.Then, recreate the Ethernet frame and 10 of the destination.0.0.Deliver the IP packet to 100.
In this way, when transmitting an IP packet, the IP packet is transferred while using a protocol called ARP.
All three agree with using ARP to resolve the MAC address, but the explanation of Kenichi and Izumi's ARP is incorrect.Kenichi -kun makes a mistake that the MAC address of other networks can be examined with ARP.The ARP request is sent by Ethernet broadcast, so you cannot send an ARP request to other networks.Izumi -chan is wrong that she switches the destination of the ARP request.She is also incorrect to transfer the ARP request with a router.The correct answer is Takeda -kun.
This article is a special feature in the August 2007 issue of Network Magazine 1 "Who can be understood in the quiz?"TCP/IP" is re -edited.The content is in principle at the time of publication, and may be different from the present. |